ความเข้ากันได้ทางเคมีของท่อ PVC คืออะไร? ท่อ PVC มีลักษณะอย่างไร?
2022-06-09|
สารบัญ |
ความเข้ากันได้ทางเคมีของท่อ PVC
เนื้อหาต่อไปนี้อ้างอิงตามความเข้ากันได้ทางเคมีของท่อพลาสติกที่ระบุไว้ในแคตตาล็อก Good Gi ฉบับปี 2019 รวมถึงความเข้ากันได้ทางเคมีของท่อ PVC คู่มือความเข้ากันได้ทางเคมีนี้จะต้องไม่สอดคล้องกับฉบับประกาศฉบับก่อนหน้าหรือในอนาคต คำแนะนำความเข้ากันได้อื่นๆ ในสิ่งพิมพ์
ความเข้ากันได้ทางเคมีของท่อพลาสติกอาจมีการเปลี่ยนแปลงเป็นครั้งคราวเนื่องจากการเปลี่ยนแปลงในกระบวนการผลิต การใช้แผนภาพเหล่านี้อย่างไม่เหมาะสมอาจส่งผลให้เกิดการบาดเจ็บหรือความเสียหายต่อทรัพย์สินได้
วิธีตรวจสอบความเข้ากันได้ทางเคมีของสารเคมีที่ระบุไว้ในท่อ Good Gi
-
ตรวจสอบตารางรหัสวัสดุ
-
ค้นหาตัวกลางหรือสารเคมีในตารางความเข้ากันได้ทางเคมีของตัวกลางและวัสดุท่อ จากนั้นค้นหารหัส (G, L, P, "-", "#")
-
อ่านคำอธิบายรหัสระดับความเข้ากันได้ตามตารางวัสดุด้านล่าง
ตารางรหัสวัสดุ
| GOODGI Thermoplastic Tubing P/N | Material | Code |
| - | High Density Polyethylene | HDPE |
| - | Flexible Nylon | N |
| GPA | Unplasticized Nylon (semi-rigid) | NR |
| - | Linear Low Density Polyethylene | PE |
| GHT, GDW | Flame Resistant Polyethylene | PEFR |
| GR | Polypropylene | PP |
| GP-100, GP-200, GP-300, GP-600 | Flexible Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | PV |
| - | Polyurethane | U |
| - | Fluorinated Ethylene Propylene | FEP |
| - | Perfluoroalkoxy | PFA |
| GND-LL, GND-SS, GND-TT | Polytetrafluoroethylene | TFE |
| GKY | Polyvinylidene Fluoride | PVDF |
ตารางความเข้ากันได้ทางเคมีของตัวกลางและวัสดุท่อ:
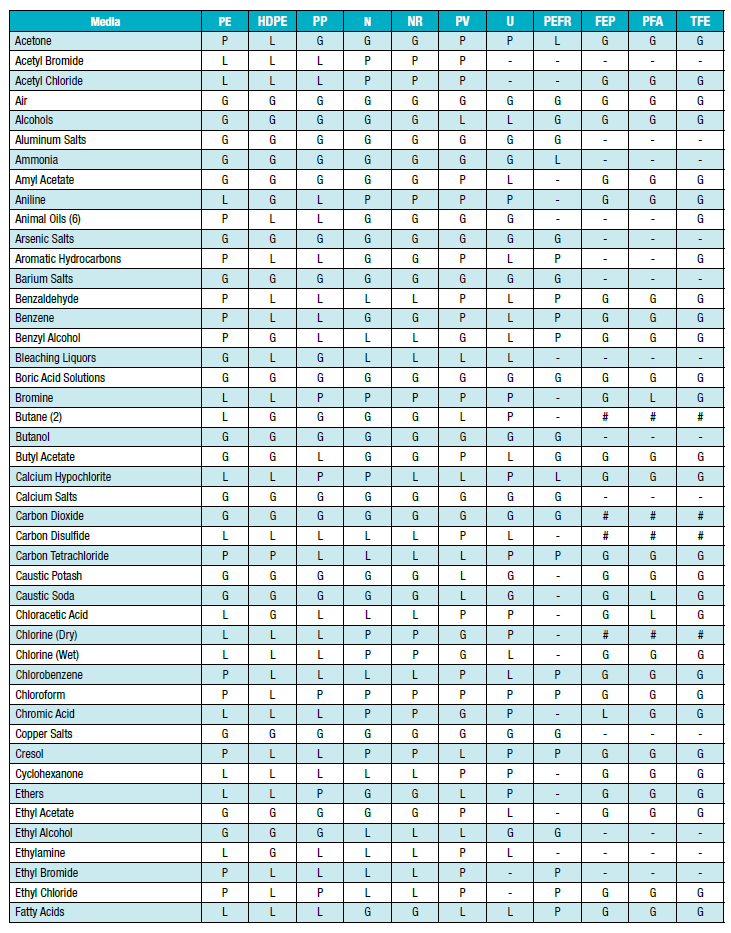
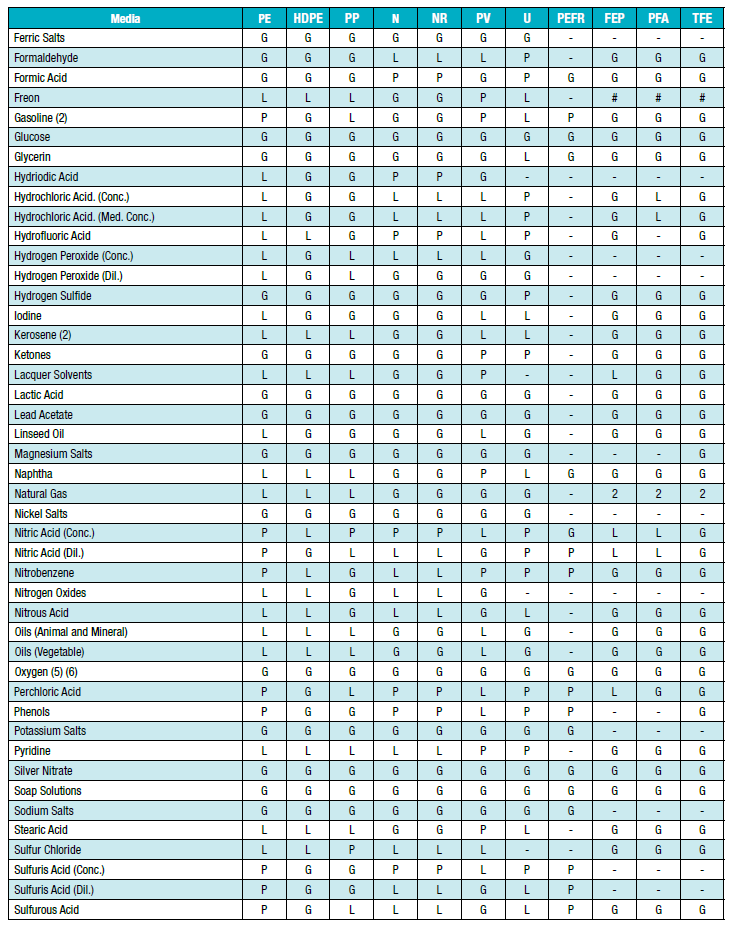
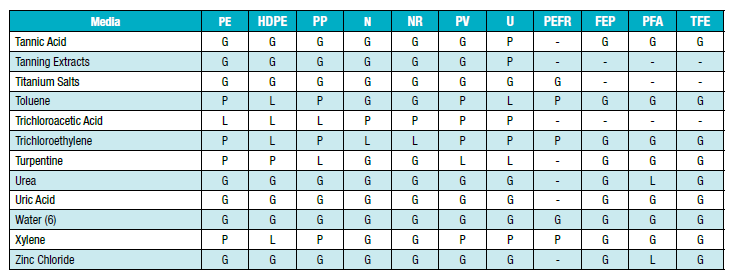
คำอธิบายรหัสระดับความเข้ากันได้
-
G:ดีถึงดีเยี่ยม - การบวม การยืดตัว หรือการเปลี่ยนแปลงพื้นผิวเกิดขึ้นเพียงเล็กน้อยหรือไม่มีเลย
-
L:แบบสำคัญหรือแบบที่มีเงื่อนไข - มีผลกระทบที่ชัดเจน แต่ไม่ได้หมายความว่าจะนำไปใช้ไม่ได้เสมอไป แนะนำให้ทำการทดสอบเพิ่มเติมสำหรับการใช้งานเฉพาะด้านและควรประเมินผลกระทบระยะยาว เช่น ศักยภาพในการแข็งตัวหรือการแตกร้าว
-
P:แย่หรือไม่เป็นที่น่าพอใจ - เข้ากันไม่ได้หรือไม่แนะนำสำหรับการทดสอบจริง
-
-:ไม่ได้รับการทดสอบ - ไม่ทราบความเข้ากันได้
-
#:สำหรับฟลูออโรโพลีเมอร์ - ทนต่อสารเคมีได้ดีแต่อาจทะลุผ่านได้
ข้อมูลเบื้องต้นเกี่ยวกับวัสดุ PVC
วัตถุดิบของท่อ PVC คือ โพลีไวนิลคลอไรด์ (ภาษาอังกฤษ: Polyvinyl Chloride ตัวย่อ: PVC) ซึ่งเป็นวัสดุโพลีเมอร์ที่ได้จากการเติมโพลีเมอไรเซชันของไวนิลคลอไรด์ เป็นพลาสติกโพลีเมอร์สังเคราะห์ที่มีการผลิตกันอย่างแพร่หลายเป็นอันดับสามรองจากโพลีเอทิลีนและโพรพิลีน
โครงสร้างทางเคมีของ PVC - -CH_{2}-CHCl-CH_{2}-CHCl-CH_{2}-CHCl- โพลีไวนิลคลอไรด์ถูกแปรรูปเป็นรูปทรงท่อในรูปแบบพื้นฐานสองรูปแบบ: แบบแข็งและแบบยืดหยุ่น
PVC แบบแข็ง เช่น ท่อน้ำ ความยืดหยุ่นทำได้โดยการเติมพลาสติไซเซอร์ (ที่นิยมใช้กันมากที่สุดคือพาทาเลต) เพื่อให้มีความยืดหยุ่นมากขึ้น
ในรูปแบบนี้สามารถใช้เพื่อพ่นปลอกหุ้มสายเคเบิล ฯลฯ และเปลี่ยนยางในการใช้งานหลายประเภท ท่อ PVC ที่ผลิตโดย Good Gi จัดอยู่ในหมวดหมู่นี้
ท่อ PVC มีลักษณะการใช้งานอย่างไร?
-
ทนต่อแรงดันไฟฟ้า
-
ทนต่อสภาพอากาศ
-
ทนต่ออุณหภูมิสูงและต่ำ
-
ต้านทานการยืดหยุ่น
-
ทนน้ำมัน
ใช้กันอย่างแพร่หลายในฉนวนกันความร้อนและการป้องกันชุดสายไฟรถยนต์ มอเตอร์และชิ้นส่วนการเชื่อมต่อสายไฟ แม้ว่าท่อ PVC จะมีฮาโลเจน แต่ความทนทานต่อการเสื่อมสภาพที่ดีเยี่ยมทำให้ยากต่อการเปลี่ยนรูปในสภาพแวดล้อมที่รุนแรง
สินค้าที่เกี่ยวข้อง
| Photo | Product Name | Rated voltage | Operating Temp. | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
ท่อพีวีซี
GP-600V
|
600V | -30℃~105℃ | UL Certification |
 |
ท่อพีวีซี
GP-300V
|
300V | -30℃~105℃ | UL Certification |
 |
ท่อพีวีซีที่มีความต้านทานต่อความเย็น
GP-600V-CR
|
600V | -40℃~105℃ | UL Certification |
 |
ท่อพีวีซีที่ไม่ใช่ UL
GP-100
|
customized | -10℃~100℃ | NO UL Certification |
 |
PVC ท่อมาร์คสาย
GMOR
|
- | -10°C~100°C | RoHS Certification |